Test of a non-dedicated distributed network
Home
: Utilise a distributed computing network to optimise the control parameters of the hybrid Monte Carlo global optimisation algorithm.
This web page is structured as follows:
- Introduction
- Case study
- History of this document
- References
Introduction
A distributed computing network here refers to a spacially distribution of computing resources. Also, a distinction may be made between
'dedicated' and 'non-dedicated' resources. Dedicated resources are typically specialised hardware whereas non-dedicated resources can be
desktop PSs sitting idle when not used by its owners.
A non-dedicated distributed network (grid) was set up at the ISIS facility.
The first test of this network was to study in detail the control parameters of the hybrid Monte Carlo (HMC) global optimisation algorithm described in [2].
Case study
The control parameters of an algorithm may crucially affect the efficiency (speed) of the algorithm.
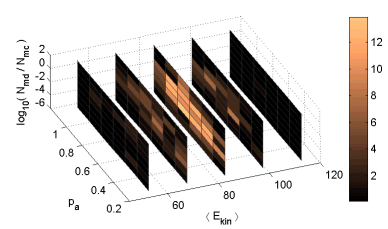
The implementation of HMC in [2] contains three such parameters. Fig. 1 shows the number of times (out of 20) that the HMC algorithm solved a given task for different values of the control parameters.
On a single 1800MHz PC it would have taken approximately six months to create the data for the plot below.
On the grid this was completed in just under two weeks.
The use of a distributed network, enabled us to optimise the control parameters of the HMC algorithm significantly faster. This exercise demonstrated the potential of distributed computing for carrying out investigations of this kind.
History or this document
The first version of this document was completed 8/11-04.
References
- A. J. Markvardsen, K. Shankland, W. I. F. David, G. Didlick, J. Appl. Cryst. 38, 107 (2005), https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889804028894
- J. C. Johnston, W. I. F. David , A. J. Markvardsen , K. Shankland, Acta Cryst. A58, 441-447 (2002), https://doi.org/10.1107/S010876730200911X